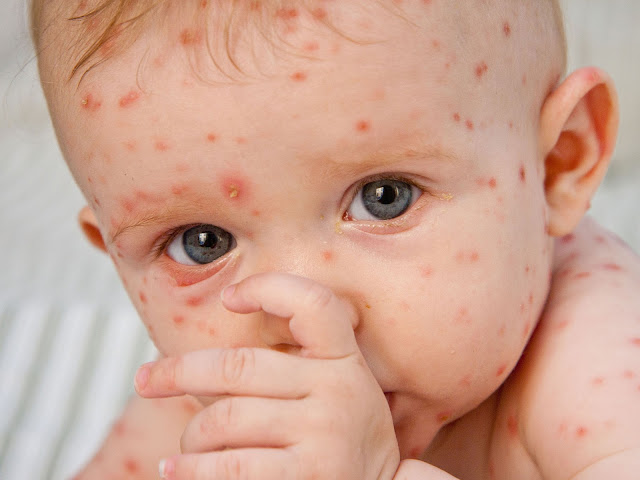
Chickenpox
Chickenpox is
a highly contagious disease
caused by the initial infection with varicella zoster virus. The
disease results in a characteristic skin rash that forms small, itchy blisters, which
eventually scab over. It is a mild and common childhood illness, but can also
occur in adults. Chickenpox is an airborne
disease which spreads easily
through the coughs and sneezes of an infected person.
Prevention and Cure
Chickenpox
can be prevented by a vaccine. Treatment usually involves relieving symptoms
although high-risk groups may receive antiviral medications.
Medications
Analgesic,
Antiviral drug, and Antihistamine
Self-care
Moisturizer
and Oatmeal bath
Specialists
Pediatrician
and Primary care provider (PCP)
Coughs, colds and ear infections in
children
Common Cold is a viral infectious disease of the upper respiratory tract that primarily affects the nose. The throat, sinuses, and voice box may also be affected. It’s normal for a child to
have eight or more colds a year.
Prevention and Cure
Most
people recover on their own within two weeks. Over-the-counter products and
home remedies can help control symptoms.
Medications
Nonsteroidal
anti-Inflammatory drug, Analgesic, Antihistamine, Eye decongestant, and Cough
medicine
Self-care
Menthol,
Nasal irrigation, and Throat lozenge
Specialists
Pediatrician
and Primary care provider (PCP)
Cough is
a sudden and often repetitively occurring reflex which
helps to clear the large breathing passages from secretions, irritants, foreign
particles and microbes.
The cough reflex consists
of three phases: an inhalation, a
forced exhalation against
a closed glottis,
and a violent release of air from the lungs following opening of the glottis,
usually accompanied by a distinctive sound.
Prevention and Cure
A hot shower can help a cough by loosening secretions in
the nose. Drinking fluids helps
to thin out the mucus in postnasal drip. Try a menthol cough drop.
Otitis is
a general term for infection of the
ear. Acute
otitis media (AOM) is the most common ear infection. Parts of the
middle ear are infected and swollen and
fluid is trapped behind the eardrum.
Prevention
and Cure
Treatment
varies and may include watchful waiting, antibiotics, or anti-inflammatory
medicines.
Most ear infections go away on their
own. Some require antibiotics.
A person may be prescribed ear drops
and advised to keep the ear dry.
The condition typically resolves
within a few weeks. Medications such as antihistamines, anti-nausea drugs, and
steroids are better.
Croup
Croup is
a type of respiratory infection that
is usually caused by a virus.
Croup can be caused by a number of viruses including parainfluenza and influenza virus.
Rarely it is due to a bacterial infection. Croup is a
relatively common condition that affects about 15% of children at some point.
Croup is very common in
children under five years old.
Prevention and Cure
Most cases
clear up with home care in three to five days. A doctor may prescribe a steroid
for a persistent case. Rarely, a severe case may need hospital care.
Supportive care
Oxygen
therapy, Can be self-healing, and Airway management. Clearing
a blocked airway of food, foreign objects, fluid and other obstructions. A top
priority in emergency situations
Medications
Analgesic,
Nonsteroidal anti-Inflammatory drug, Cough medicine, Steroid, and
Vasoconstrictor
Specialists
Pediatrician, Primary care provider
(PCP), and Emergency medicine doctor
Diarrhea and vomiting in children
Diarrhoea is
the condition of having at least three loose or liquid bowel movements each
day. It often lasts for a few days and can result in dehydration due
to fluid loss.
Infection
from viruses like rotavirus, bacteria like salmonella and, rarely, parasites
like giardia. Viruses are the most common cause of a child's diarrhea. Along
with loose or watery stools, symptoms of a viral gastroenteritis infection
often include vomiting, stomachache, headache, and fever.
Prevention and Cure
Avoid
spicy foods, fruits, and caffeine until 48 hours after all symptoms have
disappeared.
Avoid
chewing gum that contains sorbitol.
Avoid milk
for 3 days after symptoms disappear. Can eat cheese or yogurt with probiotics.
Fever in children
Fever is defined as having a temperature above
the normal range due
to an increase in the body's temperature set-point. A fever can be
caused by many medical conditions ranging
from the not serious to potentially serious. This includes viral, bacterial and parasitic infections such
as the common cold, urinary tract infections, meningitis,malaria and appendicitis among
others.
Prevention
and Cure
Place a cool, damp washcloth on your child's forehead while she
rests.
Give your child a lukewarm
tub bath or a sponge bath. As the
water evaporates from her skin, it will cool her and bring her temperature
down. Don't use cold water. It can make her shiver and cause her body
temperature to rise. Likewise, don't use rubbing alcohol. It can cause a temperature spike
and possibly even alcohol poisoning.
Offer your child plenty of fluids and chilled foods, such as
ice pops and yogurt, to help cool the body from the inside out and keep her
hydrated.
Use a fan. Again, you don't want your child to be chilled. Keep the fan at a
low setting and have it circulate the air around her rather than blow directly
on her.
Remove layers of clothing so your child can lose heat more easily
through her skin. Dress her in one light layer. If she's shivering, give her a
light blanket until she's warm again.
Food allergies in children
A food allergy is an abnormal immune response to food.
The signs and symptoms may range from mild to severe. They may include itchiness,
swelling of the tongue, vomiting, diarrhea, hives, trouble breathing, or low
blood pressure. Common
foods involved include cow's milk, peanuts, eggs, shellfish, tree nuts,
wheat, rice,
and fruit.
The common allergies in a region vary depending on the country.
Prevention and Cure
Antihistamine
drugs treat mild reactions. A severe reaction needs an injection of the drug
epinephrine and emergency room care.
Medications
Antihistamine,
Blood pressure support, and Immunotherapy.
Supportive care
Airway
management. Clearing a blocked airway of food, foreign objects,
fluid and other obstructions. A top priority in emergency situations.
Medical procedure
Desensitization
Measles
Measles is
a highly contagious infection caused by the measles virus. Initial
signs and symptoms typically include fever,
often greater than 40 °C , cough, runny nose,
and inflamed eyes.
Measles is an airborne disease which
spreads easily through the coughs and sneezes of
those infected.
Anyone can get measles if they
haven't been vaccinated or had it before, but it's most common in children.
Prevention and Cure
There's no
treatment to get rid of an established measles infection, but over-the-counter
fever reducers or vitamin A may help with symptoms.
Preventative
MMR
vaccine. A combination vaccine that protects against measles,
mumps, and rubella.
Medications
Analgesic
Specialists
Infectious
disease doctor, Pediatrician, and Primary care provider.
Mumps
Mumps is
a viral disease caused
by the mumps virus.
Initial signs and symptoms often include fever, muscle pain, headache,
and feeling tired. This
is then usually followed by painful swelling of one or
both parotid glands.
Mumps is an uncommon but
contagious viral infection. Mumps
is highly contagious and
spreads rapidly among people living in close quarters.
Prevention
and Cure
Treatment
focuses on symptom relief. Recovery takes about two weeks. The disease can be
prevented by the MMR vaccine.
Preventative
MMR
vaccine. A combination vaccine that protects against measles,
mumps, and rubella.
Medications
Analgesic
and Nonsteroidal anti-Inflammatory drug
Self-care
Bed rest. Reducing
activity for a short period of time following injury or illness to promote
healing.
Specialists
Infectious
disease doctor, Pediatrician, and Primary care provider (PCP)
Rubella
This disease is often mild with half of people not
realizing that they are sick. A rash may start
around two weeks after exposure and last for three days. It usually starts on
the face and spreads to the rest of the body. The rash is not as bright as that
of measles and
is sometimes itchy.
Prevention and Cure
Rubella
has been declared eliminated in the US. Parents are cautioned to vaccinate
children with the MMR vaccine to prevent its re-emergence.
Medications
Analgesic
Preventative
MMR
vaccine. A combination vaccine that protects against measles,
mumps, and rubella.
Supportive care
Can be
self-healing. Condition usually improves over time without
treatment.
Specialists
Infectious
disease doctor, Pediatrician, and Emergency medicine doctor
Whooping cough
Whooping cough is a
highly contagious bacterial disease.
Initially, symptoms are usually similar to those of the common cold with
a runny nose, fever,
and mild cough.
This is then followed by weeks of severe coughing fits.
Whooping cough is a highly
contagious bacterial infection and most serious in babies.
Prevention and Cure
Treatment
includes antibiotics.
Medications
Antibiotics.
Stops
the growth of or kills bacteria.
Supportive care
Monitoring
for changes or improvement. Monitoring a medical condition
instead of taking action right away.
Specialists
Pediatrician
and Primary care provider (PCP)